MULTI-ATTRIBUTE WELL INTERPOLATOR
The Multi-Attribute Well Interpolator (MAWI) adds geologically consistent detail to reservoir models by using external trends to drive interpolation of lateral changes beyond well control. This improves reservoir model quality between wells.
Building Better Low Frequency Models
The MAWI analysis accounts for variations in the low frequency model away from well control and allows geoscientists to estimate the spatial variability of the geology. By generating a quality low frequency model for inversion, MAWI enables the determination of absolute rock properties.
In MAWI, correlations are sought between multiple seismic attributes and well log data. These correlations at the well are used to build a best-fit pseudo well at each trace, based on the relative contribution of the seismic attributes at the trace location. The model is built layer by layer, using the EarthModel® FT Complete layers built from the seismic interpretation. The low frequency model is then used in seismic inversion to generate a result that is more geologically consistent.
Inclusion of a quality low frequency model allows geoscientists to determine absolute rock properties—properties that reservoir engineers can rely on when defining and executing their drilling programs.
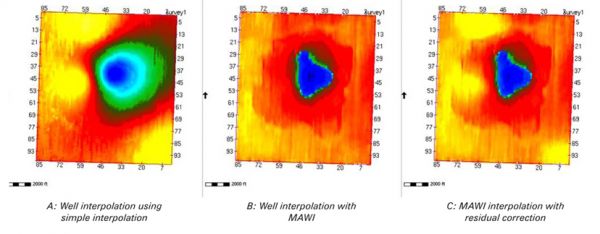
Below is an example of models of a devonian reef built with and without using MAWI.