WAVELETTOOLS
Jason has invested a great deal of resources in developing and implementing the most advanced wavelet estimation methods along with a wide variety of QC capabilities to ensure that a high-quality wavelet is obtained.
Accurate wavelet estimation is absolutely critical to the success of any seismic inversion. The inferred shape of the seismic wavelet may strongly influence the inversion results and therefore subsequent assessments of the reservoir quality. WaveletTools delivers added functionality for Wavelet Estimation.
Laterally-Variable Wavelets and Filters
Laterally varying wavelets are derived from multiple wavelets that are interpolated in the frequency domain by independently interpolating their amplitude spectra, unwrapped phase spectra and start times. Weighted interpolation schemes are employed using the X,Y coordinates of each wavelet. The resulting file (.mod file) is a volume of data type wavelet.
Q-Based Wavelets
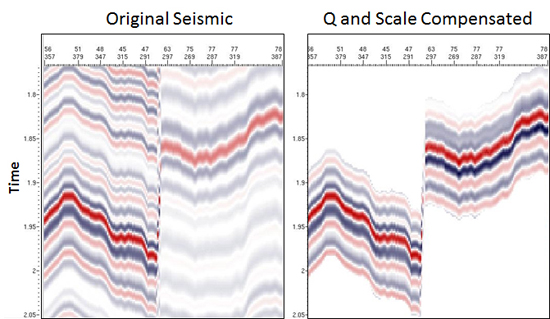
pSeismic traces show decreasing amplitudes with increasing time due to attenuation. In addition, there may be smaller amplitude changes due to seismic data processing. Using this option, you can estimate amplitude changes from both attenuation and processing.
To estimate the Q factor and the scale factor, the spectrum of the input seismic data in a moving window is compared to the seismic spectrum in a reference window. The spectral differences are used to compute the Q factor.
You can estimate the attenuation by selecting either a constant Q factor for each trace, or a Q factor that varies vertically along the traces. By QC'ing the estimated Q factor, you can validate the attenuation in the seismic data. Additionally, scaling factors are estimated in order to account for possible changes in amplitude that were applied during the seismic data processing (for example AGC and NMO correction).
The Q and scale factors can be used directly in InverTracePlus and RockTrace® to compensate for attenuation during inversion.
Deconvolution Filter Design
Deconvolution filters transform an input wavelet to another target wavelet. The filter is computed so that its convolution with the input wavelet gives the smallest least squares error relative to the target wavelet. This procedure can be used to design and apply an operator to do Coloured Inversion.