COMMINGLED WELL MODEL (CWM)
Our Commingled Well Model (CWM) is the result of many years of experience in well analysis. This package will be a powerful tool for anyone attempting to understand commingled well flow behaviour. The Software works as a predictive or as an analytical tool:
PREDICTIVE
In predictive mode the CWM can be used to model the behaviour of a new commingled completion or to look at the effect of changing an existing completion (adding perforations or shutting a zone off, for example). The model predicts the performance of each layer including overall production and crossflows between layers. In this way it acts as a powerful completion management tool.
ANALYTICAL
In analytical mode the model can be used to match well surveillance results such as production logs or distributed temperature (DTS) data. Combining this information with the well’s production history and its initial conditions allows the user to infer how reserves are distributed between layers. This facilitates optimization of production and future field development.
The software is easy to use and is available only from WTKI. It is significantly cheaper and easier to use than other softwares and can be installed easily on any PC.
To purchase a license, click download below and follow the registration process. For product support contact CWM@wtki.com.au.
CWM 2.2 INTRODUCTION
OVERVIEW
The CWM is specifically designed for modelling commingled gas wells, though it is perfectly valid for the simpler single layer case. The results of the CWM in terms of layer and well rate and pressure evolution are broadly consistent with the discussion in the classic SPE paper 01329-G: A Study of the Behavior of Bounded Reservoirs Composed of Stratified Layers (Lefkovits et al , 1959-1960).
The CWM can be used for forward modelling of the expected behaviour of a commingled well. It also incorporates a methodology for estimating the GIIP (gas initially in place) associated with each individual layer, following the workflow outlined in SPE paper 158733: Estimating Zonal Gas-in-Place in a Commingled Well Using Results from Production Logs (Last, 2012) The main features of the CWM are:
- Inflow performance calculations for each layer based on the input layer properties and a pseudo steady-state (PSS) inflow equation. The use of pseudo steady-state inflow is more in line with the method of Tempelaar-Lietz, which is referenced in the Lefkovits paper, and introduces some inaccuracies at early time in each timestep. However, as Lefkovits pointed out in his paper, the differences between a more exact solution (transient inflow transitioning to PSS) and this simplified approach are usually small.
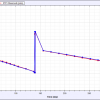
- The CWM is a time-stepping model, with the total-well gas flowrate at each timestep matched to the corresponding entry in an input Production History. At each timestep a material balance calculation&
RatingVisits2,076Redirects435Don't Miss Out! Get the Best Deal on this Software - Email Us Now!